15 Unemployment
Objectives
- Know key terms in computing unemployment: working-age population, employed, unemployed, labor force
- Compute unemployment and labor force participation rates
- Identify different types of unemployment
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Working-Age Population | Those age 16 or older who are not in the military or institutionalized |
| Employed | Those who are part of the working-age population and currently have a job |
| Unemployed | Those who are part of the working-age population, not currently working, actively searching for work, and able to accept a job if offered |
| Labor Force | The sum of employed and unemployed individuals |
15.1 Data
15.2 Unemployment Types
| Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Frictional Unemployment | Unemployment due to the time it takes for employers to search for workers and workers to search for jobs |
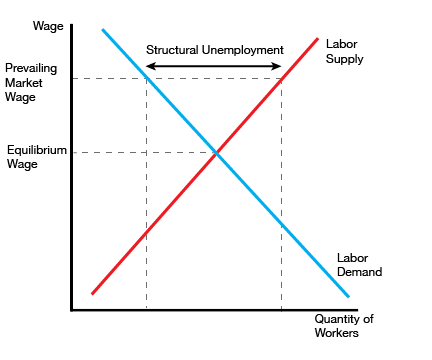
| Structural Unemployment | Unemployment that occurs because wages don’t fall to bring labor demand and supply into equilibrium |
| Cyclical Unemployment | Unemployment that is due to a temporary downturn in the economy |
15.3 Conclusion
- This lecture studies the measurement of unemployment
- We study its construction from several measures of the population
- We identify different types of unemployment (frictional, structural, cyclical)