8 Externalities
Objectives
- Identify positive and negative externalities
- Identify if the externality comes from the cost (supply) or benefit (demand) side
- Implement equilibrium in market diagram and identify equilibrium and socially optimal quantities
- Know correct policy to correct for externalities
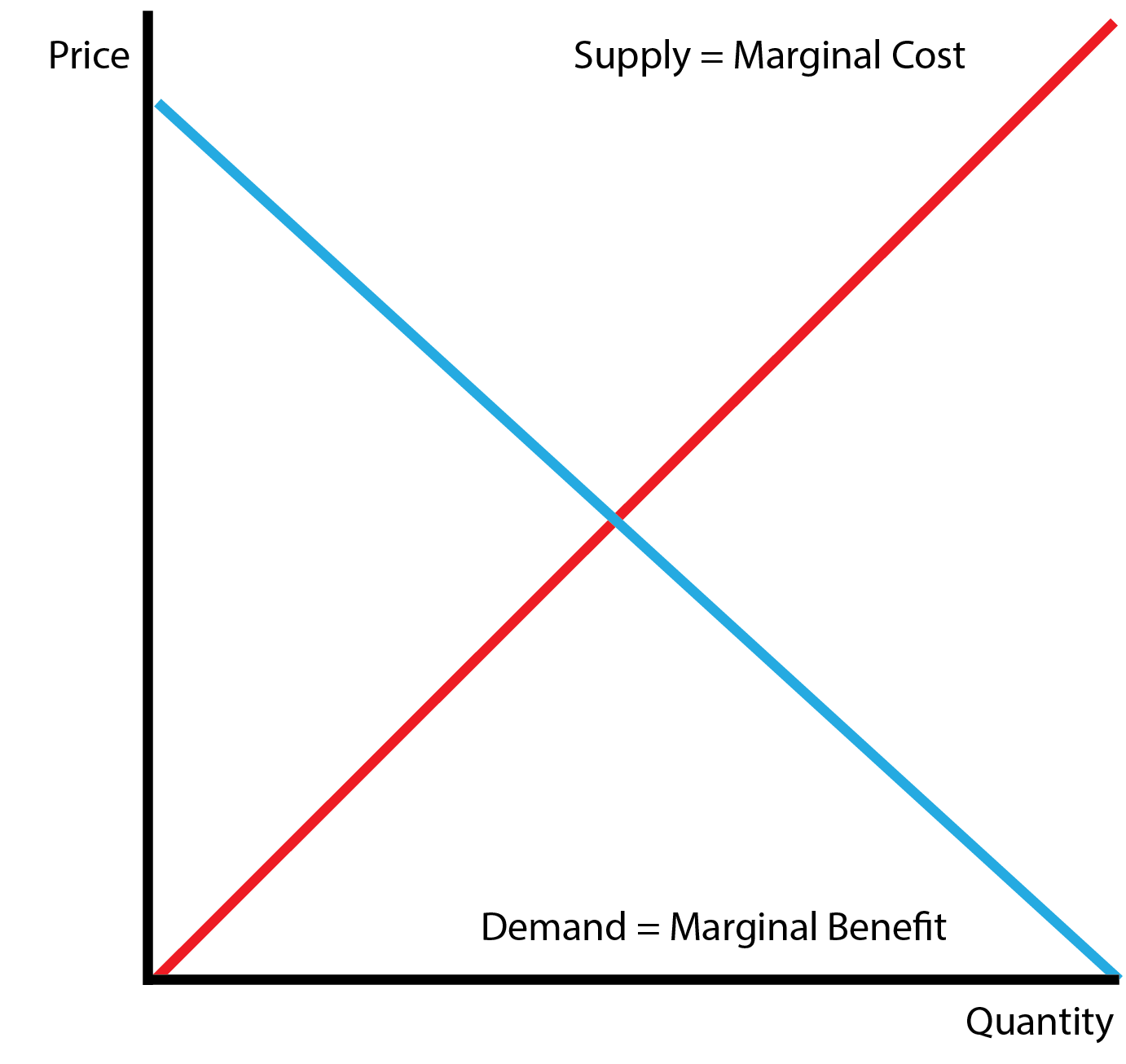
Our standard market equilibrium includes only two characters: the consumer and producer. This section studies externalities, when the production or consumption of a good impacts a bystander.
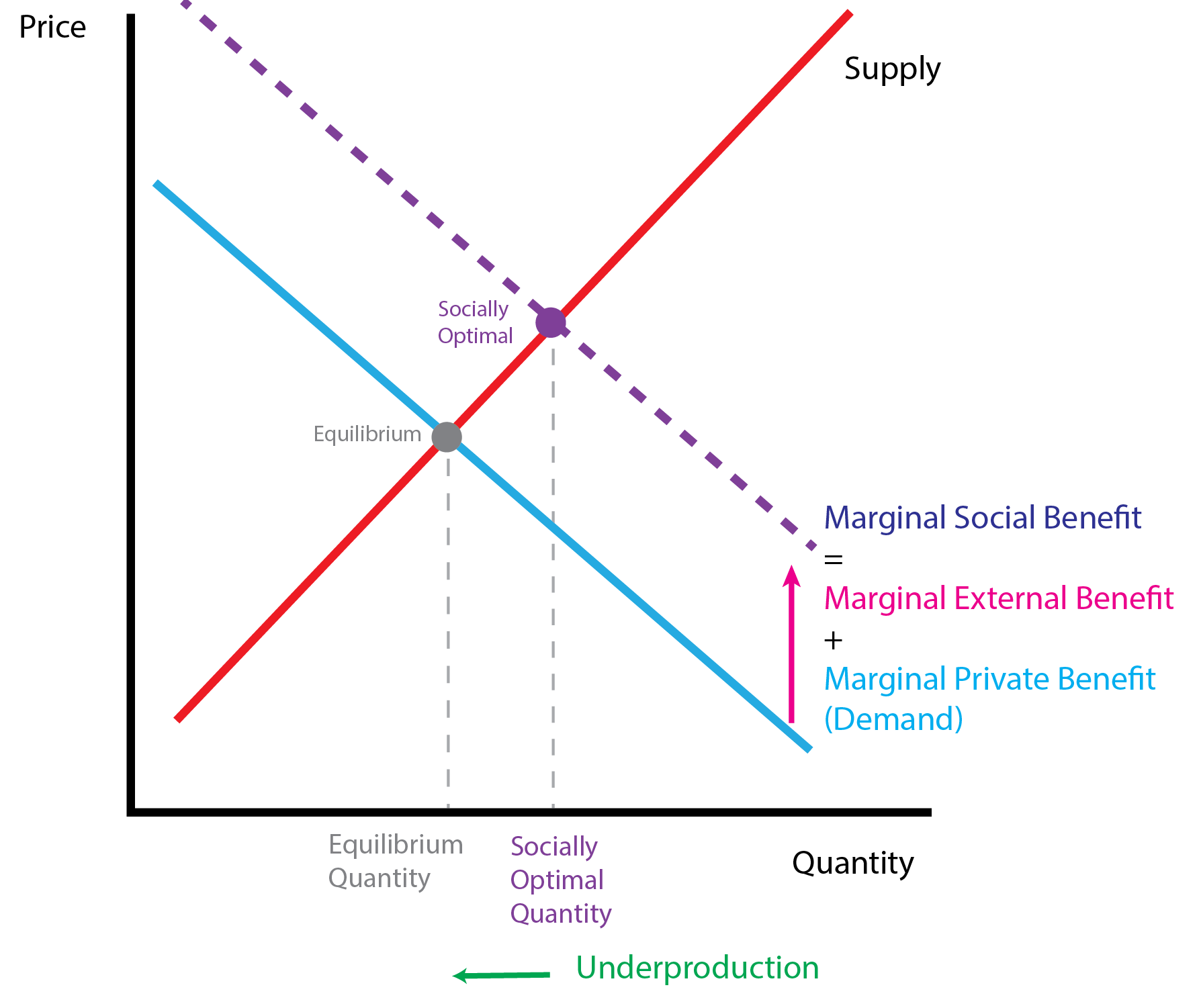
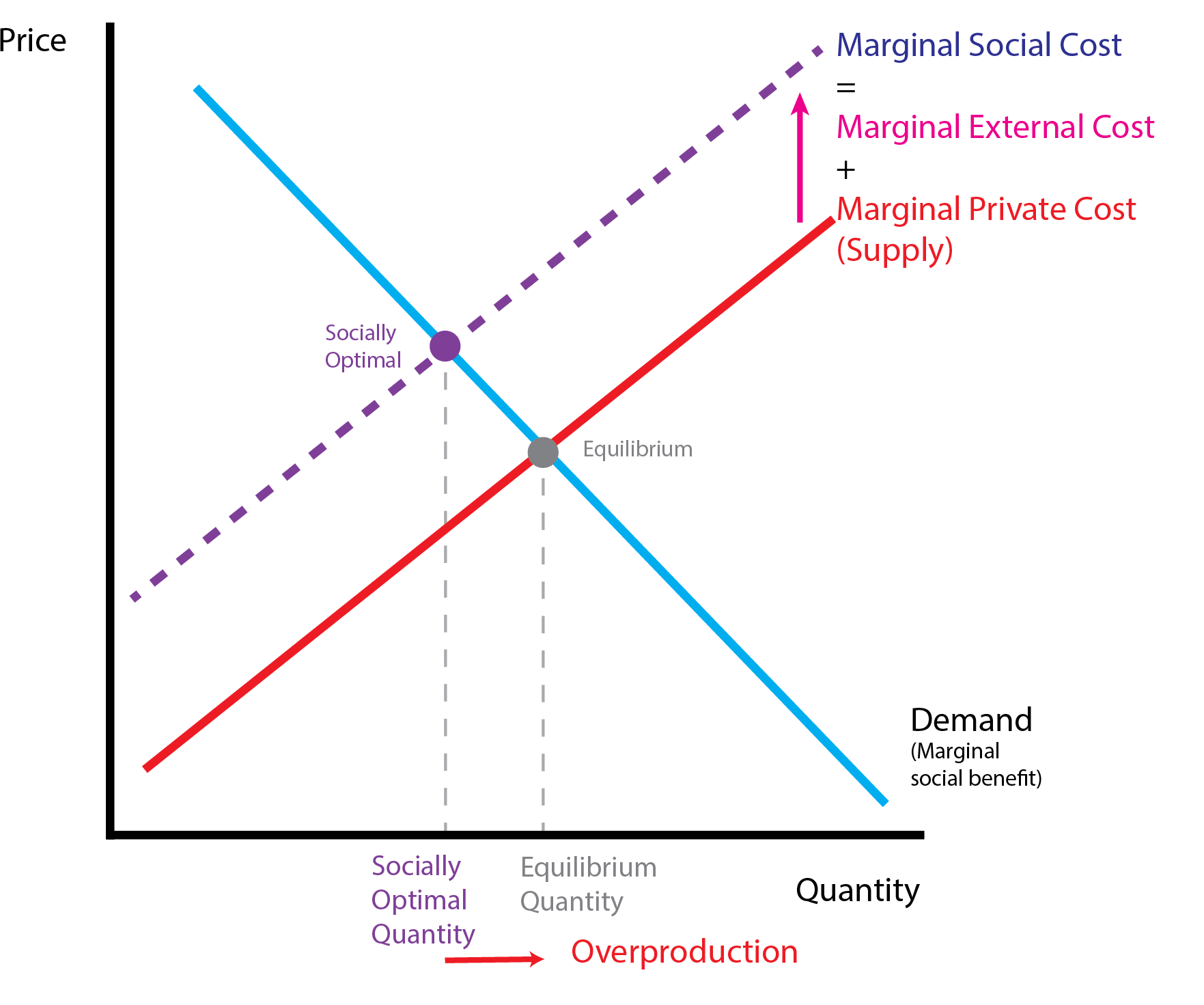
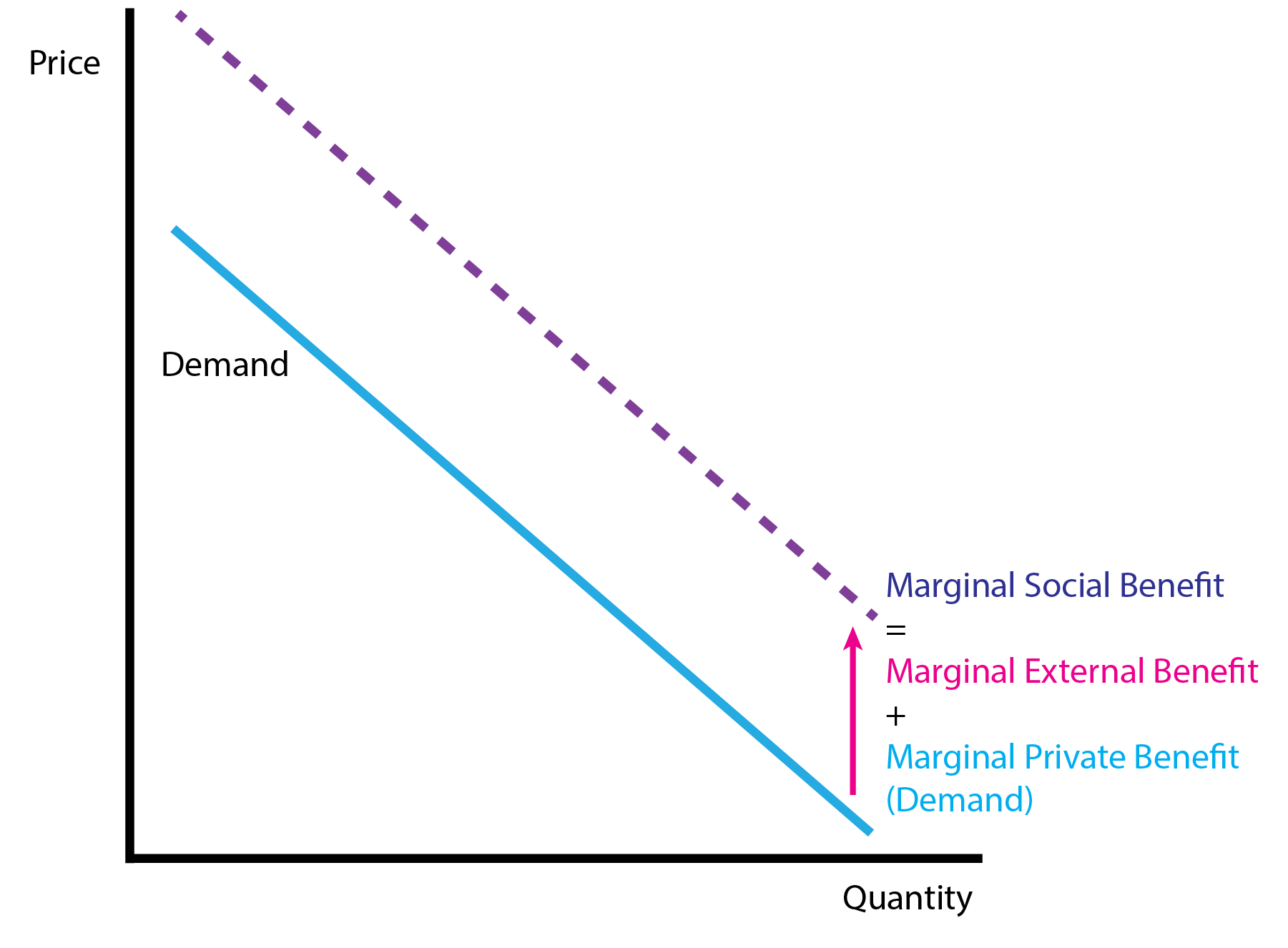
8.1 Positive and Negative Externalities
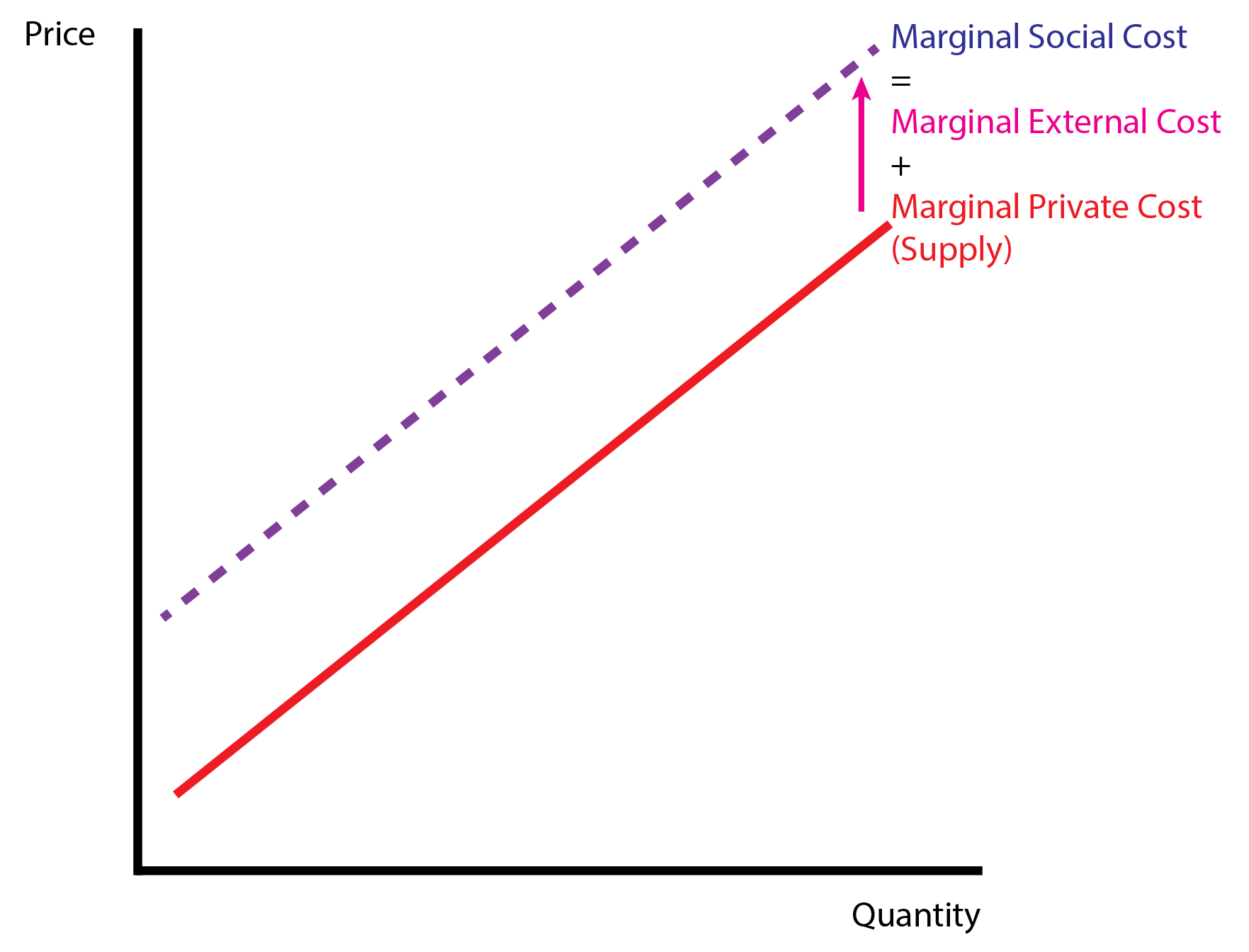
8.3 Policy: Correcting for Externalities
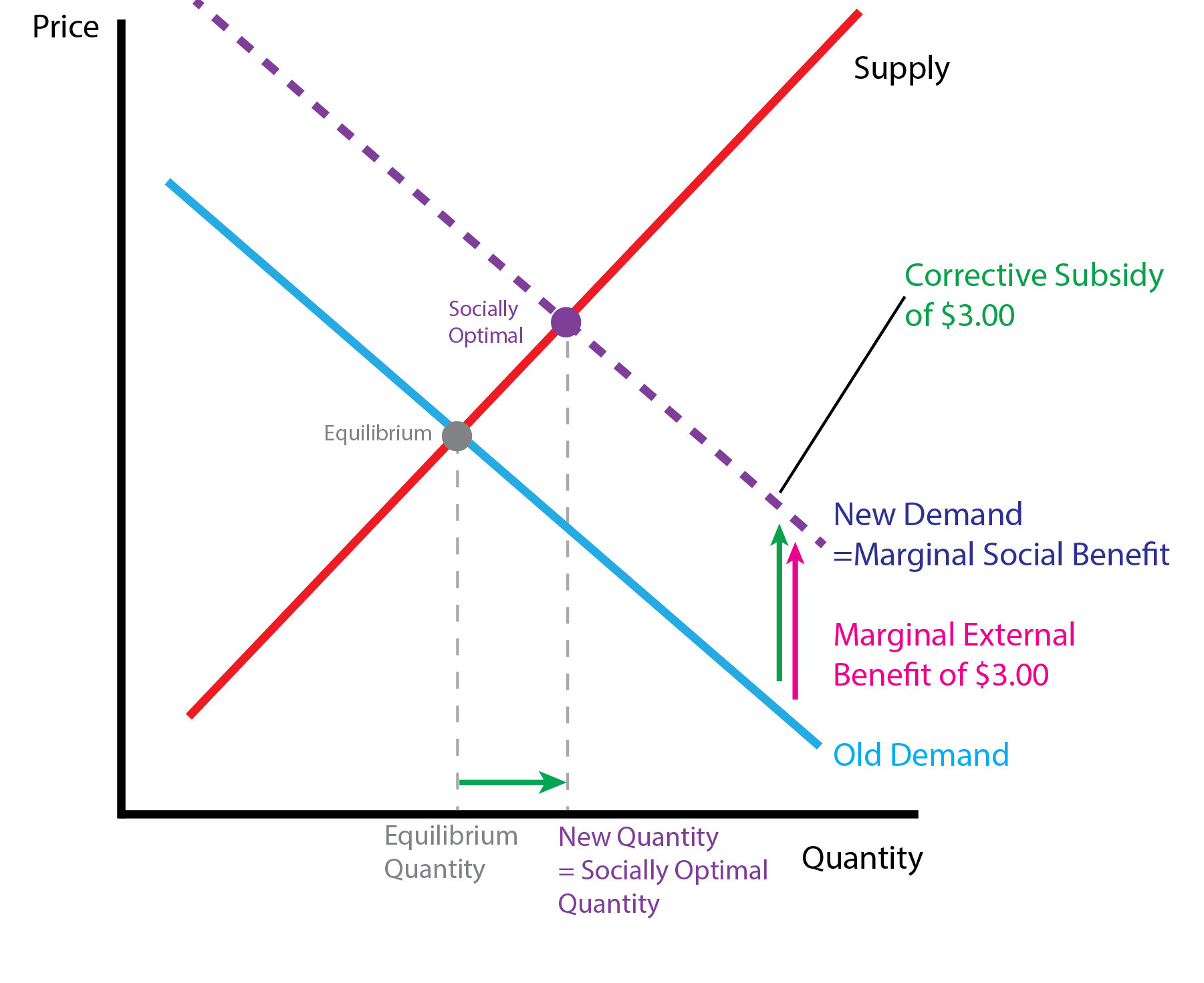
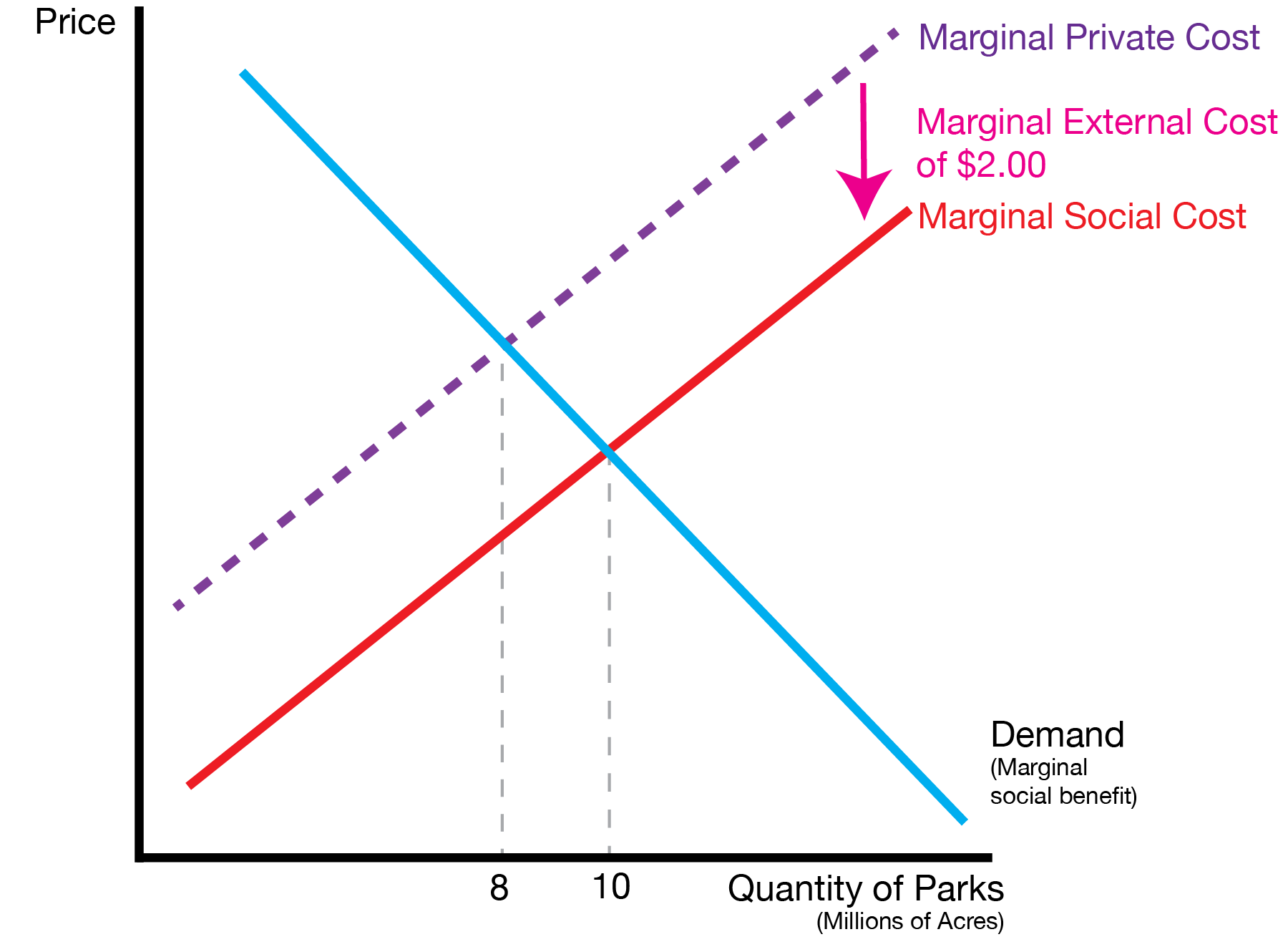
| Externality | Tax Policy |
|---|---|
| Negative | Tax |
| Positive | Subsidy |
8.4 Conclusion
- This lecture studies externalities, side effects that benefit or harm bystanders
- Externalities can modify the benefits (demand side) or costs (supply side) of bystanders
- We can correct for them by introducing taxes and subsidies